Electronic waste, or e-waste, is one of the fastest-growing waste streams in the world, and India is no exception. With the rapid technological advancements and increasing consumption of electronic devices, the e-waste problem in India has reached alarming levels. According to a report by the Global E-waste Monitor, India generated about 3.2 million metric tonnes of e-waste in 2019 alone, making it the third-largest e-waste generator in the world. This burgeoning e-waste crisis poses severe environmental and health risks, and tackling it has become a critical need of the hour. Fortunately, a number of innovative Indian startups are stepping up to address this challenge, offering sustainable solutions that could reshape the country’s approach to e-waste management.
The E-Waste Crisis in India
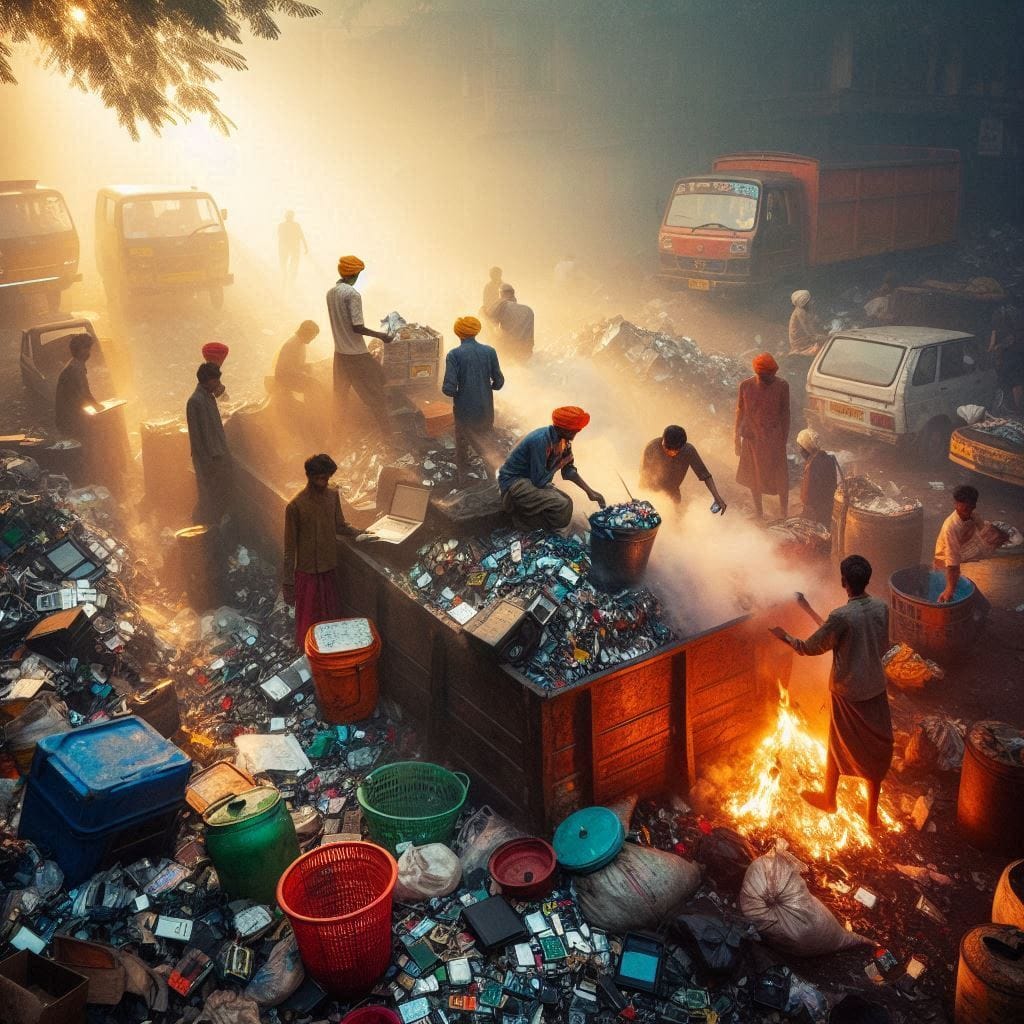

E-waste includes discarded electronic devices like smartphones, laptops, televisions, and other gadgets. These products often contain hazardous materials such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can cause severe environmental pollution if not disposed of properly. In India, the informal sector dominates the e-waste recycling industry, with around 95% of e-waste processed in unauthorized, unregulated facilities. Workers in these informal sectors often handle toxic materials without proper safety measures, leading to serious health risks.
Additionally, the lack of public awareness and inadequate infrastructure for proper e-waste management contribute to the growing crisis. The current e-waste regulations, while a step in the right direction, have not been sufficient to curb the escalating problem.
How Indian Startups Are Leading the Way
Startups in India have recognized the urgent need for innovative and scalable solutions to tackle the e-waste crisis. These startups are not only focusing on recycling and waste management but also on raising awareness and educating the public on the importance of responsible e-waste disposal. Here are some notable startups that are making a significant impact:
- Attero Recycling: As one of India’s leading e-waste management companies, Attero Recycling has developed a proprietary recycling process that recovers precious and rare earth metals from discarded electronics. Their state-of-the-art facilities ensure that e-waste is processed in an environmentally friendly manner, minimizing the harmful effects on the ecosystem.
- Karo Sambhav: This startup is creating a circular economy for electronic products by facilitating responsible e-waste collection and recycling. Karo Sambhav collaborates with manufacturers, brands, and other stakeholders to implement sustainable e-waste management solutions. They focus on building awareness and providing incentives for consumers and businesses to dispose of their e-waste responsibly.
- Cerebra Green: Cerebra Green is addressing the e-waste problem through its integrated approach that covers collection, recycling, refurbishment, and disposal of electronic waste. The company aims to reduce the environmental impact of e-waste by refurbishing and reselling old electronics, thereby extending their lifespan and reducing the demand for new devices.
- BinBag: BinBag offers an end-to-end e-waste management solution, focusing on small and medium enterprises (SMEs). They provide a convenient and compliant way for companies to dispose of their e-waste while ensuring data security and environmental responsibility.
The Impact of Startups on the Environment

The efforts of these startups are beginning to show positive results. By introducing organized and regulated e-waste management practices, these companies are reducing the amount of e-waste that ends up in landfills or is processed in hazardous conditions. For instance, Attero Recycling has successfully processed over 500,000 tonnes of e-waste, recovering valuable materials and preventing harmful substances from polluting the environment.
Moreover, startups like Karo Sambhav are fostering a culture of responsibility and sustainability. Through education campaigns and take-back programs, they are encouraging consumers to rethink their electronic consumption habits and consider the environmental impact of their actions. This shift in mindset is crucial for the long-term success of e-waste management in India.
Challenges and the Way Forward
Despite the progress made by startups, the road ahead is still fraught with challenges. The informal sector’s dominance in e-waste recycling, coupled with inadequate enforcement of regulations, continues to hinder the efforts of formal recycling initiatives. Additionally, the lack of consumer awareness and reluctance to pay for proper disposal services remain significant barriers.
To overcome these challenges, there is a need for stronger policy support, stricter enforcement of e-waste regulations, and increased public awareness campaigns. Government initiatives, such as the Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) guidelines, need to be effectively implemented and monitored to ensure compliance by manufacturers and consumers alike.
Furthermore, collaboration between startups, government bodies, and large corporations will be essential in building a comprehensive and sustainable e-waste management ecosystem. By leveraging technology and innovation, India has the potential to not only tackle its own e-waste problem but also set an example for other developing nations.
Conclusion
The rising e-waste crisis in India is a complex problem that requires a multifaceted approach. Startups are playing a crucial role in addressing this issue through innovative solutions, education, and responsible recycling practices. However, to achieve lasting change, a collective effort from all stakeholders, including the government, businesses, and the public, is essential. By working together, India can transform its e-waste challenge into an opportunity for sustainable growth and environmental protection.
For more insights on sustainable business practices, explore our articles on Epic Infinite, where we delve into the latest trends in environmental sustainability and innovative solutions. Learn more about how technology is reshaping industries and contributing to a greener future.